“ איילונית - אין לה לא קנס ולא פיתוי
There is no fine for the rape or seduction of an Aylonit
”
Aylonit Syndrome
An Aylonit is a woman who is congenitally unable to have childern. In the fifth chapter of Niddah (47b) the Mishnah describes the signs which suggest that a woman is an Aylonit:
תלמוד בבלי נדה דף מז עמוד ב
...בת עשרים שנה שלא הביאה שתי שערות, תביא ראיה שהיא בת עשרים שנה - והיא איילונית, לא חולצת ולא מתיבמת
A woman who is twenty years old and has not grown two pubic hairs..is classified as an Aylonit...
Earlier in our current tractate, Ketuvot (11a), the Talmud suggested the etymology of the word Aylonit: "איילונית - דוכרנית דלא ילדה - an Aylonit [is given this name] as if she is a ram [דכר is the Aramic translation of the Hebrew word איל– a ram] which [being a male] cannot give birth"
In the last tractate that we studied (Yevamot 80b) the Talmud gives four other signs of this condition, which are codified by Maimonides:
רמב"ם הלכות אישות פרק ב הלכה ו
ואלו הן סימני אילונית, כל שאין לה דדין, ומתקשה בשעת תשמיש, ואין לה שיפולי מעיים כנשים, וקולה עבה ואינה ניכרת בין איש לאשה
These are the signs that a woman is an Aylonit: She has not developed breasts, she has difficulty during sexual intercourse [that is, she has a diminished libido], the mons pubis is lacking, and she has such a deep voice that it is indistinguishable from that of a man...(Mishneh Torah, Hil. Ishus, 2:6)
There are many reasons for a woman to be infertile, but because the Talmud lists a number of signs other than infertility, we are able to narrow down the possible causes in the special case of the Aylonit. As many have previously noted, the cause of the Aylonit is likely to be what, (since 1938) we now call Turner's Syndrome.
Turner's Syndrome
In 1938 an American endocrinologist names Henry Turner published a paper describing a newly observed syndrome in seven female patients. (A syndrome is a series of medical abnormalities which occur together.) It consisted of a triad of infantilism, a webbed neck, and a deformity of the elbow. It was found only in female patients, and was associated with delayed or absent sexual development. We now know (and Turner did not) that it is caused by a genetic aberration in which the patient has a missing X chromosome. Instead of carrying 44 regular and two X chromosomes, a woman with (what we now call) Turner's Syndrome has one missing X chromosome. (It gets a little more complicated: in some cases of Turner's Syndrome the woman has only part of one of the X chromosomes missing. And in others, the women's cells contain a mixture of both normal - 45XX - and abnormal - 45X - chromosomes. This is called mosaicism. But let's keep our focus.)
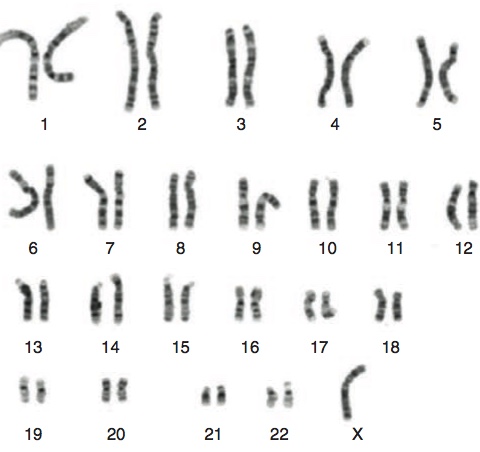
Sex chromosome analyses in Turner's Syndrome. Here the 22 pairs of autosomes are grouped according to size and the sex chromosomes placed at the end; in this case, there is only one X chromosome. From Saenger and Bondy. Turner Syndrome. In Sperling M. (ed.) Pediatric Endocrinology. Pittsburgh PA, Elsevier 2014.
Turner's Syndrome occurs in about 1 out of every 2,000 live-born girls. In addition to infertility in most, there are liver problems, high blood pressure, cardiac disorders and various metabolic disorders. Most of the girls with Turner's Syndrome have skeletal abnormalities and a short stature. In girls with the 45X variant, there is ovarian failure and hence infertility, although the cause is not yet clear.
The variable appearance of Turner syndrome. Both of these 7-year-old girls with short stature have the 45X variant of Turner syndrome. The girl on the left was diagnosed at birth due to prominent neck webbing and low-set and posteriorly rotated ears. She also has micrognathia and a low posterior hairline. In contrast, the girl on the right was diagnosed at age 7 due to short stature without “classical” stigmata of Turner syndrome, and she is more typical of the clinical presentation of the majority of girls with Turner syndrome diagnosed in the 21st century. From Saenger and Bondy. Turner Syndrome. In Sperling M. (ed.) Pediatric Endocrinology. Pittsburgh PA, Elsevier 2014.
“Girls and women with Turner syndrome may have low self-esteem and more shyness and social anxiety than controls. In a population-based study of 566 French women with Turner syndrome, low self- esteem was associated with hearing impairment and limited sexual experience, whereas age at first sexual intercourse was related to age at puberty and paternal socioeconomic class.”
A study of Polish women with Turner's Syndrome, found that these women had less "...interest in males, less frequent sexual activity, later initiation of sexual life and a less frequent orgasm rate." Other studies found that women with this syndrome were less likely to establish a relationship with a partner, and were less sexually active than women from the general population. All this suggests that the Talmud's description in which they suffer from "difficulties during intercourse" (מתקשה בשעת תשמיש) may be correct.
Let's remember that behind these scientific findings are real women with the same range of sensitivities, feelings, hopes and aspirations as those of us who have two functioning sex chromosomes. Let's give the last word to Harley Gould, a researcher at the National Institutes of Health:
“Moreover, it is important to remember that society continues to dis- criminate against people that are different, and that being short, or infertile, or looking different impose quite a social burden on individuals... Our demonstration of very similar academic, employment...suggests that genomic imprinting of X-linked genes has little to do with functioning in school or socially...We would like to add to that concept the positive observation that many individuals with Turner Syndrome display excellent coping skills, including perseverance in the face of adversity and equability of temperament.”