Herod the Weird
Today's page of Talmud contains a bizarre account of the sexual proclivities of Herod the Great, the Jewish Roman King who died in 4 BCE. Herod took a fancy to one of the women in the House of the Hasmoneans, where he was a slave. He led a rebellion, killing all members of the Hasmonean house but the one woman of his desires. Then comes this:
בבא בתרא ג, ב
כי חזת ההיא ינוקתא דקא בעי למינסבה סליקא לאיגרא ורמא קלא אמרה כל מאן דאתי ואמר מבית חשמונאי קאתינא עבדא הוא דלא אישתיירא מינייהו אלא ההיא ינוקתא וההיא ינוקתא נפלה מאיגרא לארעא טמנה שבע שנין בדובשא איכא דאמרי בא עליה איכא דאמרי לא בא עליה
When she saw that he [Herod] wanted to marry her, she went up on to a roof and cried out "...I am throwing myself down from this roof." He preserved her body in honey for seven years. Some say that he practiced necrophilia with her, others that he did not...
While studying Bava Kamma we discussed the medicinal properties of honey. We noted that although the Talmud described honey as being harmful to your health, it is in fact very good for you. It has antibiotic and antiviral properties, helps with a cough, and has been claimed as a therapy for dozens of medical conditions. In today's page of Talmud we can add another use for honey: to preserve body parts. Or even whole bodies.
Honey as a MEDICAL Preservative
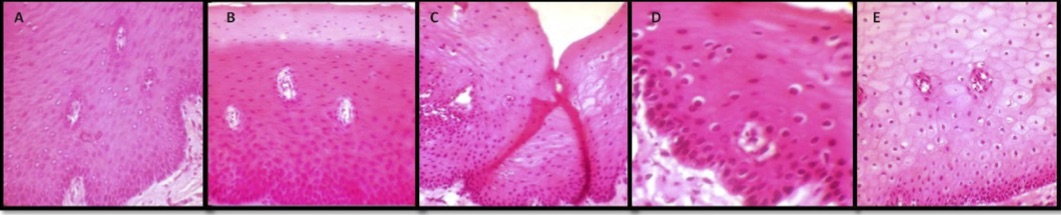
Dr. Shankargouda Patil is a senior lecturer at the Ramaiah Dental College in Bangalore, India, and has published two papers on honey as a preservative. In one experiment Dr. Patil took "commercially available fresh goat meat" and placed each bit into containers containing either formalin, water, honey or jaggery syrup. (Jaggery syrup being a coarse brown Indian sugar made by evaporating the sap of palm trees.) After waiting all of twenty-four hours he then processed the tissues and stained them as you would any medical specimen. He noted that although formalin is routinely used to preserve medical specimens, it is highly toxic. And as I recall from my days in the lab, highly smelly. So it makes sense to see if there are alternative preservatives. Like honey.
Photomicrograph of the tissues fixed in: A. Formalin, B. Honey, C. Sugar syrup, D. Molasses syrup, E. Distilled water (H & E, 40X). From Patil S, Premalatha B R, Rao R S, Ganavi B S. Revelation in the Field of Tissue Preservation – A Preliminary Study on Natural Formalin Substitutes. J Int Oral Health 2013; 5(1):31-38.
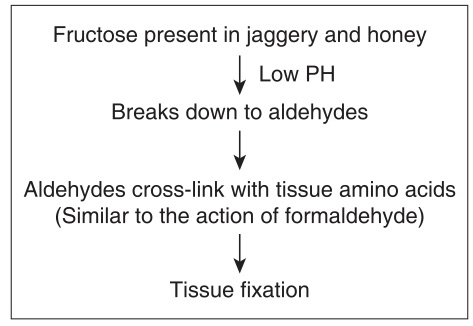
Patil notes that honey's high osmolarity, low pH and the presence of components such as hydrogen peroxide and phenol inhibine in it all contribute to its anti-oxidative and antibacterial effect. Here is how he thinks honey works as a fixative:
From Patil S, Premalatha B R, Rao R S, Ganavi B S. Revelation in the Field of Tissue Preservation – A Preliminary Study on Natural Formalin Substitutes. J Int Oral Health 2013; 5(1):31-38.
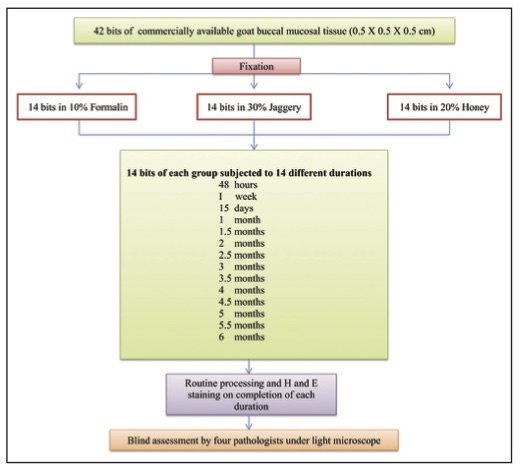
Ever keen to push the boundaries of honey as a medical preservative, Dr Patil published a second paper titled Natural sweeteners as fixatives in histopathology: A longitudinal study. This time he studied the fixative property of jaggery and honey over a six-month period and compared them with formalin as a control.
From Patil S, et al. Natural sweeteners as fixatives in histopathology: A longitudinal study. Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine 2015, 6 (1); 67-70
Macroscopic appearance of tissues after 6 months of fixation with: (a) Formalin, (b) jaggery, and (c) honey. From Patil S, et al. 2015.
The conclusion from all this was that at the end of six months, honey was as good a fixative as formalin. In addition, the tissues preserved in honey had no significant odor, while the formalin preserved tissues were "pungent." On the down side though, honey left the tissues a light-brown color, while formalin caused no color change. But all this is small potatoes compared to Herod's efforts to preserve an entire human corpse. And it turns out that Herod wasn't the only one who carried out this rather peculiar exercise.
“הדבש נראה שיש לו שתי סגולות האחת למהר למחות ולכלות הדברים הנחתכים הנופלים לתוכו. והשניה להעמיד ולקיים הדברים הנחתכים הנטמנים בתוכו”
IT JUST GOT WEIRDER
Human female fetus (a) 20 weeks gestational age before and, (b) after embalming for one month in honey. From Sharquie K.E. Najim R.A. Embalming with honey. Saudi Med J 2004; 25 (11). 1755-1756.
In a paper published in 2004 in the Saudi Medical Journal, researchers from the medical college of Baghdad took these experiments to a whole new level. They preserved mice, rabbits and then ... two human fetuses in honey, to evaluate the embalming qualities of honey.
After embalming the 2 human fetuses in honey for one month and leaving them to dry at room temperature, they were mummified and shrunken. The weight of the first fetus changed from 500gm to 115gm while the second fetus weight changed from 400g to 95g. Both fetuses were darker in color. Both fetuses were observed for a period of one year without any change in their shape despite being kept at room temperature.
In case you were wondering, the authors note that "the protocol for the research project was approved by the ethical committee at the College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq. For human fetuses embalming, the nature of the experiment was explained to the parents and their approval was taken, to use the fetus for the experiments." Well that makes me feel a whole lot better.
Preserving Human Corpses in Honey
In her entertaining book Stiff: The Curious Lives of Human Cadavers, Mary Roach wrote that "in twelfth-century Arabia, it was possible to procure an item known as a mellified man. The verb to mellify" she continues, "comes from the Latin for honey, mel. Mellified man was dead human remains steeped in honey." Vicki Leon picks up the story in her equally entertaining book How to Mellify a Corpse: And Other Human Stories of Ancient Science and Superstition.
It had long been common knowledge that the Babylonians embalmed with wax and honey. But the big news began when Alexander the Great died at age thirty-three. Always organized, Alex had left pre-need instructions to mellify his remains. The high sugar content of honey draws water from cells and gradually dehydrates tissues. Thus, if honey happens to surround a corpse, under the right conditions it produces a drying action while also preserving. It seemed to work for Alex. His body survived a 1,000-mile road trip, a corpse-napping and decades-long display u a glass coffin in Memphis, Egypt - and he was still being called 'lifelike' when last seen centuries later by Roman Emperor Carcalla.
The story of Herod's sexual proclivities with a dead body recounted in today's page of Talmud are, I hope, wildly exaggerated. But the ability of honey to preserve a dead body are, it turns out, quite likely to be true. Just try to forget all this by next Rosh Hashanah.