Sunset from Clearwater Florida, Jan 29, 2020. Photo from the Talmudology archive.
We are studying the tractate Bava Basrsa (The Last Gate), which is currently dealing with the circumstances under which the sale of goods may be voided. The Mishnah (83b) ruled that if there is agreement to sell red wheat (שחמתית) and it was found to be white (לבנה), both the seller and the buyer have legal grounds to retract. The Talmud then discusses the names for these colors: what we call red and white are called "like the sun" and "like the moon." Rav Pappa (the Babylonian sage who died in 375CE) took this a step further:
בבא בתרא פד,א
בצפרא דחלפא אבי וורדי דגן עדן בפניא דחלפא אפתחא דגיהנם – ואיכא דאמרי איפכא
In the morning it becomes red as it passes over the site of the roses of the Garden of Eden, [whose reflections give the light a red hue]. In the evening the sun turns red because it passes over the entrance of Gehenna, whose fires redden the light. And there are those who say the opposite [in explaining why the sun is red in the morning and the evening, i.e., in the morning it passes over the entrance of Gehenna, while in the evening it passes over the site of the roses of the Garden of Eden.]
Shmuel ben Meir, known as Rashbam (d. ~1158) explained that "our eyes are not able to discern the colors very well because in the middle of the day the light is blinding. But in the morning and the evening, when the sun is less bright, we can see the redness of the sun."
מאור עינינו אינו ברור כל כך מתוך אור היום שמכהה עינינו אבל צפרא ופניא שהיום חשוך ניכר אדמומית החמה ורב פפא לפרש משנתנו בא אמאי מקרי שחמתית
According to Rav Pappa, the true color of the sun is red - but this true color can be seen only when the sun is at its least intense - in the evening and the morning. We have all experienced Rav Pappa's description: who cannot be moved by the sight of a blazing red sunrise or sunset? But what is the scientific explanation of these colors?
“דְּאָמַר רַבִּי חִיָּיא בַּר אַבָּא אָמַר רַבִּי יוֹחָנָן: מִצְוָה לְהִתְפַּלֵּל עִם דִּמְדּוּמֵי חַמָּה. וְאָמַר רַבִּי זֵירָא: מַאי קְרָאָה — ״יִירָאוּךָ עִם שָׁמֶשׁ וְלִפְנֵי יָרֵחַ דּוֹר דּוֹרִים״
Rabbi Chiyya bar Abba said that Rabbi Yochanan said: It is a mitzva to pray with the reddening of the sun. And Rabbi Zeira said: What is the verse that alludes to this? “Let them fear You with the sun and before the moon, generation after generation” (Psalms 72:5)…”
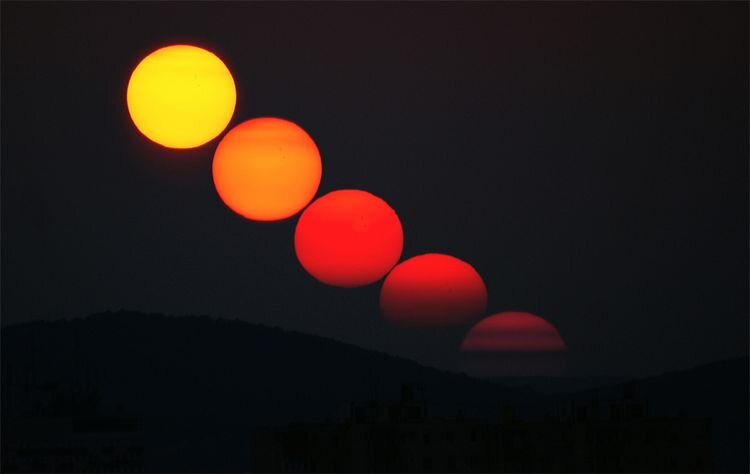
The sequence above shows the setting Sun dipping toward the western horizon. As the Sun sinks lower, its color becomes more reddened. From here.
Why sunrise & sunset are red - the science
Here is the scientific explanation. At sunrise and sunset the light from the sun is not directly overhead, but from its position on the horizon it must pass through more of the atmosphere to reach our eyes, as you can see here.
From here.
You may recall that ever since Newton and his prism we have known that white light is made up of many different wavelengths, or colors of light (Figure 1 below). As the sun’s white light passes through our atmosphere, the shorter wavelengths of light are scattered (Figure 2). And the longer the path through our atmosphere, the more the shorter wavelengths of light are scattered away from the original white sun beam. All of that scattered light (Figure 3) is from the shorter, blue end of the spectrum, which is what colors the sky blue (whatever else your dad may have told you). The remaining unscattered light is at the red end of the spectrum, and that’s why the sun appears red at sunrise and sunset, and why the clouds that reflect it are colored red.
From here.
The Color of the Sun in Space, and on Earth
According to NASA experts (who really are rocket scientists, among other things), the sun emits all colors of the visible light spectrum. And when you mix all these colors together you get...white. If you were to look at the sun from high in space, (perhaps aboard the International Space Station), it would indeed appear to be a pure white. Like this:
It was in the seventeenth century that Isaac Newton used a prism to split the sun's light into its constituent colors. Before then it was raindrops that did the same thing, forming a rainbow as a result.
Isaac Newton divided a ray of sunlight with a prism in a series of experiments published in 1672. Lego recreation is from here.
“Here on Earth, the atmosphere plays a role in the color of the sun. Since shorter wavelength blue light is scattered more efficiently than longer wavelength red light, we lose some of the blue tint of the sun as sunlight passes through the atmosphere. In addition, all wavelengths of visible light passing through our atmosphere are attenuated so that the light that reaches our eyes does not immediately saturate the cone receptors. This allows the brain to perceive color from the image with a little less blue – yellow. ”
The Cultural determinants of the Sun's Color
On their website, the NASA scientists claim that "sometimes the display color of the Sun is culturally determined. If a kindergartener in the USA colors a picture of the Sun, they will usually make it yellow. However, a kindergartener in Japan would normally color it red!" The rabbis of the Talmud had their own cultural explanation of the colors of the sun. As we have seen, after suggesting that the color of the sun may actually be white (because that is the color of a patch of skin with zora'at, usually identified as a kind of leprosy), the Talmud then explains the cause of the red sunrises and sunsets:
ולמאי דסליק דעתין מעיקרא הא קא סמקא צפרא ופניא בצפרא דחלפא אבי וורדי דגן עדן בפניא דחלפא אפתחא דגיהנם
In the morning it becomes red as it passes over the site of the roses of the Garden of Eden, whose reflections give the light a red hue. In the evening the sun turns red because it passes over the entrance of Gehenna, whose fires redden the light...
Without the scientific understanding we have today, the Talmud claimed that the red color of sunrise and sunset was due to the light filtering though the red roses of the Garden of Eden, and fires of Hell.
is the Garden of Eden real or metaphorical?
It would seem that the Talmud's description of the locations of the Garden of Eden and the Gates of Hell is to be taken literally, for it is given as an explanation for physical phenomena. But here is where things can get tricky. The famous rabbi Joseph Hayyim of Baghdad (1834–1909) wrote a work that is widely read by Sephardic Jews to this day called Ben Ish Hai. He also published three volumes of responsa between 1901 and 1905 called Rav Pe’alim. (A fourth volume was posthumously published in 1912.) In an undated question, R. Hayyim was asked about the location of the Garden of Eden. In one tradition, the garden was located “on the other side of the world,” somewhere below the equator in the southern hemisphere. However, the questioner continued, the world has been circumnavigated, and the Garden of Eden has not been identified. Where then is it located?
In his answer, R. Hayyim digressed into the truth claims of science, and then returned to the location of the Garden of Eden. He noted that although it may be located on the Earth itself, it existed on a different spiritual plane and would therefore not be perceived by the human senses. I suppose many moderns would agree with the suggestion that the Garden of Eden is not to be found in a geographic location. But today's page of Talmud reminds us that at least in talmudic Babylon, the Garden of Eden was not just a metaphor. It determined the very colors of the sun.
The Poet and the Scientist
Science is not the only way of understanding the world. Artists, poets, philosophers and religions all add different kinds of knowledge about the very same physical world that science explains. Science explains that a red sunrise is a result of physics. Rabbi Chiyya explained that it is because the sun reflects the red roses of the Garden of Eden. Which explanation most satisfies your mind? And which most satisfies your heart?
“In philosophy [i.e.science] one must proceed from wonder to no wonder, that is, one should continue one’s investigation until that which we thought strange no longer seems strange to us; but in theology, one must proceed from no wonder to wonder, that is…[until] that which does not seem strange to us does seem strange, and that all is wonderful.”















![L'atmosphère_-_météorologie_populaire_-_[...]Flammarion_Camille_bpt6k408619m.jpeg](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/54694fa6e4b0eaec4530f99d/1490796746066-SZ91FZ3ZAN8PSKGAXUKI/L%27atmosph%C3%A8re_-_m%C3%A9t%C3%A9orologie_populaire_-_%5B...%5DFlammarion_Camille_bpt6k408619m.jpeg)